
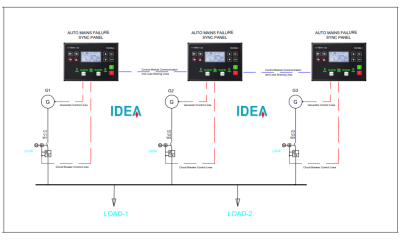
Multiple Generator Synchronization
It is especially suitable for businesses with a demand power of 800kVA and above, which are not affected by instantaneous outages in grid outage/re-energization situations. In addition, in terms of investment, the cost of a single generator set over 800kVA may be more favorable in synchronous system generator sets consisting of two, three or even more sets from time to time. It will also provide the user with significant savings in items such as fuel cost, maintenance and spare parts in cases where a significant portion of the demand power is not required (interruptions in time periods with low load density such as weekend outages, official-religious holidays).
In multi-generator synchronization systems, after the grid power is cut off, all generators in the system (even if the load density of the operation is low) start up and start feeding the load by synchronizing the other generator set(s) to the master generator connected to the first dead bus.At the end of a user-set period of time, the synchronous gensets look at the total amount of load fed and decide how many synchronous gensets can feed the current load at the end of a set period of time, and if there are any generator(s) that are not needed at that moment, they are disabled and only enough generators for the load are activated and activated. If there is a load demand approaching the adjustable percentage of the total genset reserve capacity in the system, the deactivated gensets are started one by one to ensure that only enough power is available for the load.
IDEA generator offers solutions for all synchronous systems from single grid – single generator, synchronization of multiple generators and multi-generator – multi-grid synchronous systems.
We provide project design, design, production and commissioning services in accordance with the desired operating scenario in MV/LV systems in accordance with the specification or single line scheme.
Synchronization of multiple generators is especially suitable for businesses with a demand power of 500 kVA and above, which are not affected by instantaneous interruptions in grid outage/re-energization situations.
In addition, in terms of investment, the cost of a single generator set above 500 kVA may be more favorable in synchronous generator sets consisting of two, three and sometimes even more sets. It will also provide the user with significant savings in fuel costs, maintenance and spare parts in cases where a significant portion of the demand power is not required (outages at the weekend when the load is low, outages in situations with low load density such as official-religious holidays).
In multi-generator synchronization systems, after the grid power is cut off, all generators in the system (even if the load density of the operation is low) start up and start feeding the load by synchronizing the other generator set(s) to the master generator connected to the first dead bus. At the end of a user-set period of time, the synchronous gensets look at the total amount of load fed and decide how many synchronous generators can feed the current load at the end of a set period of time and if there are any generator(s) that are not needed at that moment, they are disabled and only enough generators to feed the load are activated. If there is a load demand approaching the adjustable percentage of the total genset reserve capacity in the system, the deactivated gensets are started one by one to ensure that only the power required by the load is available in the system.
Synchronous systems also provide advantages in initial installation costs, operation, maintenance, fuel and spare parts costs.
